Search Engine Optimization SEO (2025): The Complete Guide for Beginners

Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Welcome to the ultimate resource on Search Engine Optimization (SEO). This blog, “The Complete Guide for Beginners,” will walk you through everything you need to know about SEO in 2025. Designed for beginners, it uses easy English and covers essential topics in detail. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of Search Engine Optimization and how to use it effectively.
What is Search Engine Optimization (SEO)?
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the process of improving a website’s visibility on search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo. SEO helps websites rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs), attracting more traffic and boosting business.
For beginners, think of Search Engine Optimization as a roadmap to make your website attractive to search engines. The better your SEO, the easier it is for people to find your site.
Why is SEO Important in 2025?
In 2025, Search Engine Optimization remains crucial for online success. With millions of websites competing for attention, effective SEO ensures your content stands out. Beginners and experts alike benefit from implementing strategies outlined in “The Complete Guide.”
Key Benefits of SEO for Beginners
Increased Website Traffic: Better rankings mean more visitors.
Improved User Experience: Good SEO focuses on making websites user-friendly.
Cost-Effective Marketing: Unlike paid ads, organic traffic from Search Engine Optimization is free.
Enhanced Credibility: High rankings build trust with users.

Types of Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Understanding different types of SEO is essential for beginners. This section of “The Complete Guide” will introduce you to the main types:
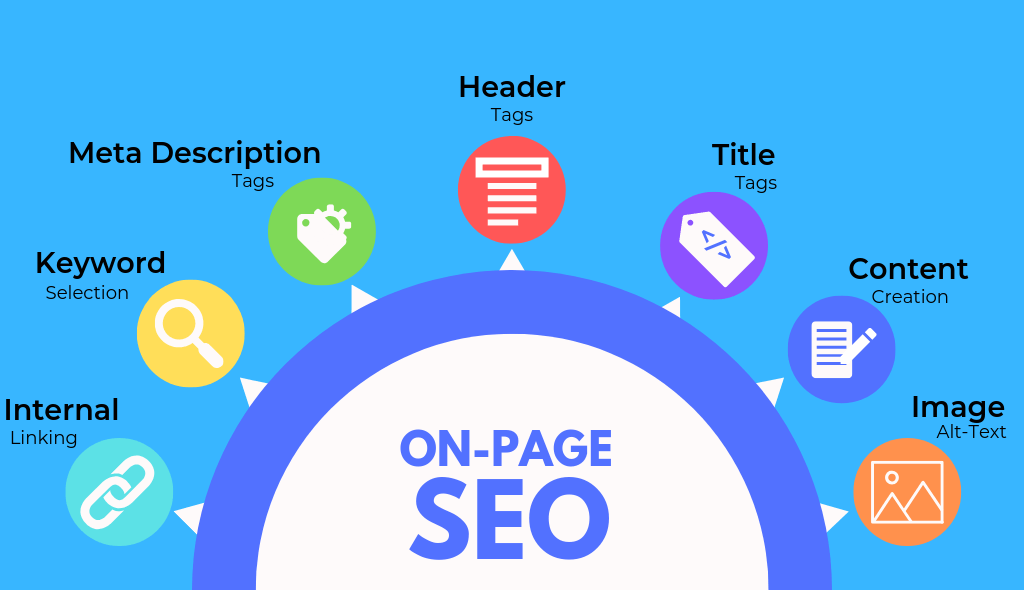
1. On-Page SEO
On-Page SEO focuses on optimizing individual pages to rank higher. Key elements include:
- Keyword Optimization: Use relevant keywords like “Search Engine Optimization” and “The Complete Guide.”
- Content Quality: Create plagiarism-free, high-quality content.
- Title Tags and Meta Descriptions: These help search engines understand your page.
2. Off-Page SEO
Off-Page SEO involves actions taken outside your website to improve rankings. These include:
Backlinks: Links from other websites that boost your credibility.
Social Signals: Shares and likes on social media.
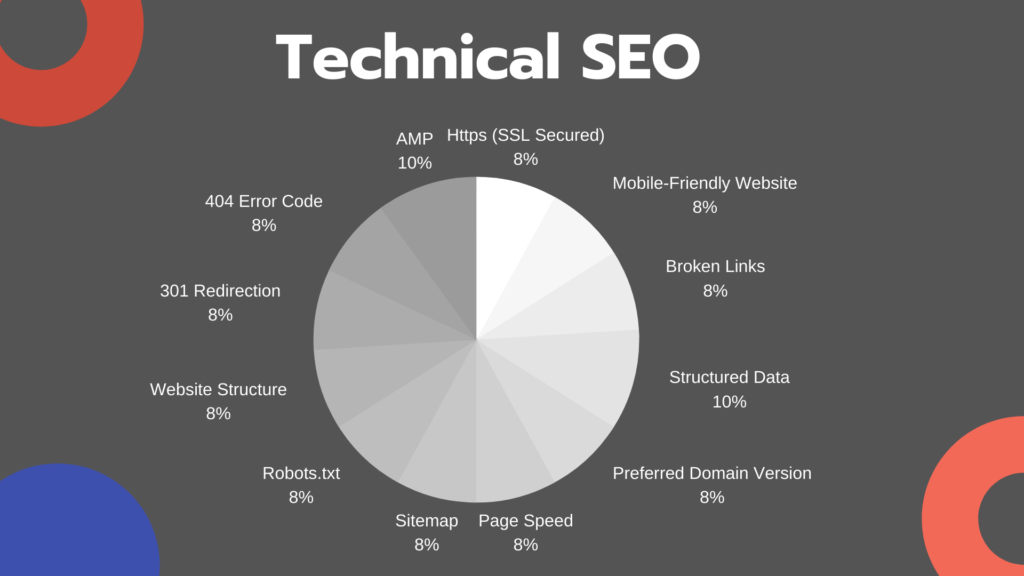
3. Technical SEO
Technical SEO ensures your website meets search engine requirements. Key aspects include:
Website Speed: Faster loading times improve rankings.
Mobile Optimization: Ensure your site works well on mobile devices.
How to Start with SEO: The Complete Guide for Beginners
Starting with Search Engine Optimization can feel overwhelming. This section simplifies the process for beginners, offering practical steps.
Step 1: Keyword Research
Keywords are the foundation of SEO. Use tools like Google Keyword Planner to find relevant keywords, such as “Search Engine Optimization” and “The Complete Guide.”
Step 2: Optimize Your Website
Create Quality Content: Use keywords naturally and avoid keyword stuffing.
Add Internal Links: Link to other pages on your site.
Improve Readability: Use short paragraphs, bullet points, and headings.
Step 3: Build Backlinks
Reach out to other websites and ask them to link to your content. Backlinks are vital for improving your SEO rankings.
Step 4: Monitor and Improve
Use tools like Google Analytics to track your progress. Regular updates to your content help maintain high rankings.
Common SEO Mistakes to Avoid
Even beginners can succeed in Search Engine Optimization by avoiding these common pitfalls:
Ignoring Mobile Optimization: Ensure your site is mobile-friendly.
Overusing Keywords: Use terms like “The Complete Guide” naturally.
Neglecting Analytics: Track your progress to improve over time.
Skipping Quality Content: Always prioritize valuable, original content.
The Complete Checklist for Beginners
Here’s a handy checklist for beginners to succeed in Search Engine Optimization:
Keyword Research: Identify your focus keywords, such as “SEO” and “Search Engine Optimization.”
Content Creation: Write informative, plagiarism-free blogs.
Technical SEO: Fix broken links and improve site speed.
Backlinks: Build high-quality backlinks from credible sites.
Analytics: Use tools to measure your success.
Conclusion
In 2025, mastering Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is essential for online success. This blog, “The Complete Guide for Beginners,” has covered everything you need to know, from the basics to advanced tips. By following these steps, even beginners can achieve significant results.




